Containment and Isolator Systems in the Pharmaceutical Industry: Ensuring Safety and Sterility
In the pharmaceutical industry, safety and sterility are paramount, both for ensuring drug efficacy and protecting the health of workers involved in manufacturing. With the increased use of highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs) and the need for stringent aseptic environments, the adoption of containment systems and isolator technology has become essential. These systems not only prevent contamination of products but also protect workers from exposure to hazardous substances.
This blog delves into the importance of containment and isolator systems in pharmaceutical manufacturing, their working principles, types, and benefits.
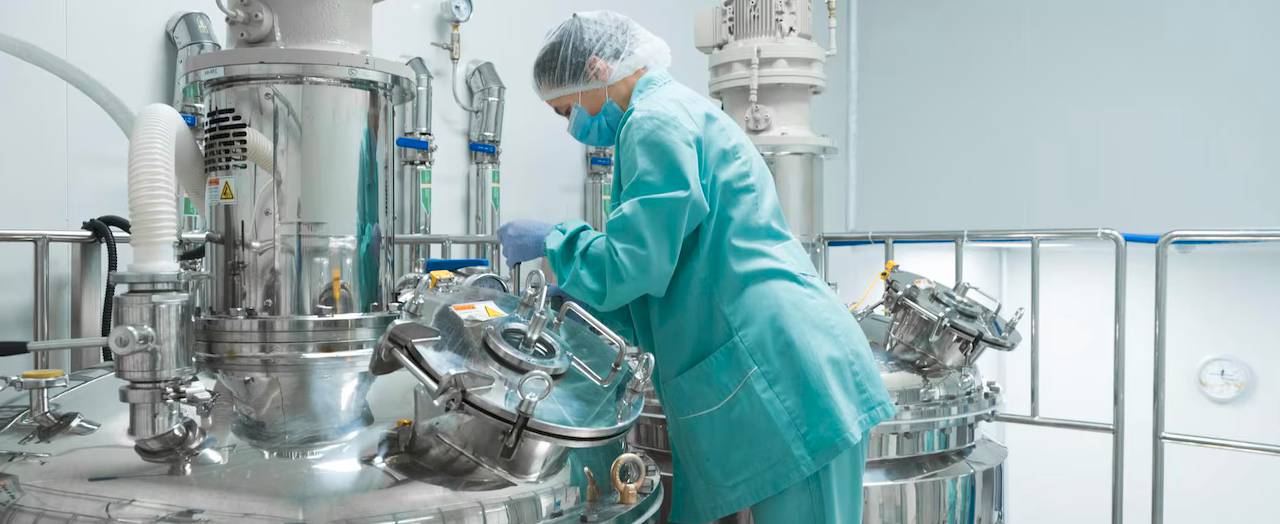

What are Containment and Isolator Systems?
Why Containment and Isolators are Essential in Pharma
Protecting Personnel
Many pharmaceutical products contain toxic or highly potent compounds that pose health risks to operators. Containment systems and isolators protect workers from exposure to these harmful substances, ensuring their safety.
Ensuring Product Integrity
In aseptic processing, maintaining sterility is critical to avoid contamination that could compromise the quality and safety of the final product. Isolators create controlled environments that minimize contamination risks and ensure product integrity.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with global regulatory standards like EU GMP Annex 1 (for sterile production), Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines, and other local or international regulations is crucial for pharmaceutical manufacturers. Isolators and containment systems help companies meet these stringent guidelines.
Key Types of Containment and Isolator Systems
1. Open Containment Systems
Open containment systems are designed to control the spread of contamination within a designated space but do not fully enclose the process. These systems often employ airflow control, extraction systems, and other engineering controls to confine hazardous materials.
Examples include:
- Biological Safety Cabinets (BSCs): Widely used in microbiology and virology labs, BSCs offer protection for operators, products, and the environment by controlling airflow and filtration.
- Fume Hoods: Used in laboratories where volatile chemicals are handled, fume hoods capture and vent harmful gases, ensuring operator safety.
While these systems are suitable for low-to-medium containment needs, they are not ideal for handling highly potent APIs or aseptic processes, where higher levels of isolation and sterility are needed.
2. Closed Containment Systems
Closed containment systems offer complete enclosure of the manufacturing process, with no direct exposure to the external environment. These systems are ideal for handling hazardous compounds or manufacturing sterile products.
Examples include:
- Closed Transfer Systems (CTS): These systems are used for transferring materials from one container to another without exposure to the surrounding environment, ensuring a high level of containment.
- Blenders and Mills with Integrated Containment: Often used in the production of oral solid dosage forms, these systems prevent the release of dust or powders during blending or milling operations.
3. Isolator Systems
Isolators represent the highest level of containment and are widely used in sterile manufacturing processes where product contamination must be avoided. They can be categorized into the following types:
- Aseptic Isolators: Designed for sterile manufacturing and aseptic processing, these isolators create a contamination-free environment for critical operations like filling, sealing, and compounding. They use overpressure and HEPA filters to ensure air purity, and the interior is often sterilized using vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP) or other decontamination agents.
- Containment Isolators: These isolators are used to handle highly potent or toxic APIs. They ensure that no airborne contamination escapes into the surrounding environment, protecting both operators and the product.
- Hybrid Isolators: Some isolators are designed to provide both aseptic and containment features, making them versatile for applications requiring sterile and hazardous material handling.
Components and Working of Isolator Systems
Glove Ports
One of the defining features of isolators, glove ports allow operators to manipulate the equipment and materials inside the isolator without breaking containment. The gloves are typically made of materials resistant to chemicals and pathogens.
Air Handling and Filtration Systems
Isolators rely on a sophisticated air handling system that includes HEPA filters to ensure that air entering and exiting the isolator is free from contaminants. For aseptic processes, the isolator environment is maintained under positive pressure, while containment isolators handling hazardous materials often operate under negative pressure.
Transfer Systems
Rapid Transfer Ports (RTPs) are used to introduce or remove materials and equipment into and out of the isolator without compromising the sterile or contained environment. These ports allow the movement of components while maintaining containment.
Decontamination Systems
Vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP) is a common sterilization method used in isolators. The VHP decontaminates all internal surfaces, ensuring that the isolator is free from microbes before aseptic operations begin.
Benefits of Containment and Isolator Systems
One of the primary benefits of containment systems and isolators is the protection they offer to operators, particularly when handling toxic or potent APIs. The closed environment of isolators, along with negative pressure control in containment isolators, ensures that harmful substances do not escape, mitigating health risks for personnel.
In sterile manufacturing, contamination is a constant risk. Isolators provide a sterile environment by eliminating the need for operators to directly interact with critical processing steps, significantly reducing contamination risks. This results in higher-quality products and fewer batch failures.
Global regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, have strict guidelines for sterile manufacturing and containment. Isolators and containment systems help companies meet these requirements, ensuring compliance with EU GMP Annex 1, PIC/S guidelines, and ISO 14644 standards.
While the initial investment in isolator systems may be high, they offer long-term cost savings by reducing product contamination, batch rejections, and the need for expensive cleanroom environments. In many cases, isolators can reduce the size of cleanrooms needed for sterile manufacturing, lowering operating costs.
Containment systems help minimize the release of harmful chemicals, solvents, and APIs into the environment. By keeping hazardous materials contained, pharmaceutical companies can reduce their environmental footprint and comply with environmental regulations.